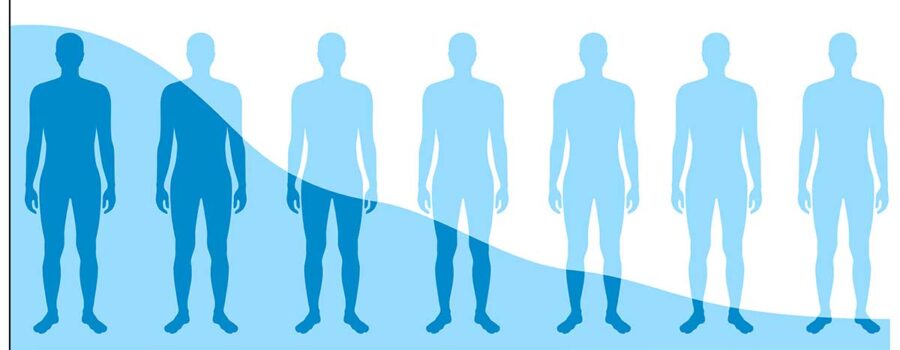
In recent years, there has been a silent epidemic of low testosterone in men affecting all age groups. While low testosterone has traditionally been associated with aging, an alarming trend has emerged: more and more teens and young men in their 20s and 30s are experiencing testosterone levels that would typically be expected in men pushing 60. This issue is not only surprising but also deeply concerning, as testosterone is a vital hormone that influences many aspects of health and well-being.
Understanding Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone responsible for the development of male reproductive tissues, the promotion of secondary sexual characteristics like increased muscle and bone mass, and the regulation of mood and energy levels. It is produced mainly in the testicles and, to a lesser extent, the adrenal glands. Optimal testosterone levels are crucial for maintaining muscle mass, bone density, red blood cell production, and overall physical and mental health.[1]
Symptoms of Low Testosterone
When testosterone levels drop, men can experience a wide array of symptoms that affect their quality of life. These symptoms include:[2]
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and low energy levels.
- Depression: Mood swings, irritability, and feelings of sadness.
- Decreased Libido: Reduced sexual desire and performance issues.
- Muscle Loss: Difficulty in maintaining or building muscle mass.
- Weight Gain: Increase in body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Cognitive Decline: Problems with memory and concentration.
These symptoms are often overlooked or attributed to other factors, which can delay proper diagnosis and treatment.
The Shocking Reality for Young Men
Recent studies and clinical observations have revealed that many young men are experiencing testosterone levels that fall into the 200s and 300s nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL).[2] For context, a healthy testosterone range for men under 40 is typically between 400 and 700 ng/dL. These abnormally low levels in young men are startling and indicative of underlying health issues that need urgent attention.
Contributing Factors
Several factors contribute to this worrying trend:
- Lifestyle Choices: Sedentary lifestyles, poor diet, and lack of exercise are significant contributors. Processed foods, high sugar intake, and inadequate physical activity can lead to obesity and insulin resistance, both of which are detrimental to testosterone production.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to endocrine disruptors found in plastics, pesticides, and certain personal care products can interfere with hormone production. These chemicals can mimic or block hormones, leading to imbalances.
- Stress: Chronic stress leads to elevated cortisol levels, which can suppress testosterone production. The modern, fast-paced lifestyle exacerbates this issue with its constant demands and pressures.
- Sleep Deprivation: Poor sleep quality and insufficient sleep have been linked to lower testosterone levels. Sleep is crucial for the body’s recovery and hormone regulation.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Conditions such as insulin resistance, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome directly impact testosterone levels. Insulin resistance, in particular, hampers the production of the enzyme AMPK, which is essential for energy balance and metabolic function.
The Importance of Awareness and Action
Awareness of this silent epidemic is the first step toward addressing it. Men need to be informed about the importance of maintaining healthy testosterone levels and the potential signs of low testosterone. Regular check-ups and hormone screenings can help detect issues early.
Taking proactive steps to improve lifestyle choices can significantly impact testosterone levels and overall health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in whole foods, adequate sleep, stress management, and reduced exposure to environmental toxins are all crucial measures.
Final Thoughts
Low testosterone in young men is a growing concern that requires immediate attention. It is not just about maintaining physical vitality but also about safeguarding long-term health. By recognizing the signs and making necessary lifestyle changes, men can enhance their well-being and prevent the detrimental effects of low testosterone.
Stay informed, take action, and prioritize your health to combat this silent epidemic.
References:
- Nassar, George N., and Stephen W. Leslie. “Physiology, Testosterone.” StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, 2024. PubMed, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526128/.
- Sizar, Omeed, et al. “Male Hypogonadism.” StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, 2024. PubMed, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532933/.